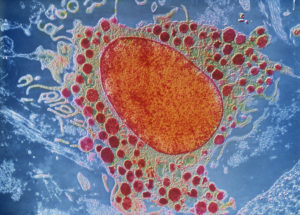
^BMast cell,^b coloured transmission electron micrograph (TEM). Mast cells are a type of white blood cell found in connective tissue. The large oval (orange) is the cell’s nucleus, which contains its genetic information. Within the cell’s cytoplasm (green) are granules (red) containing chemical mediators, including histamine and heparin. When the mast cell is activated, either by an allergic reaction or in response to injury or inflammation, these granules are released into the tissues. Histamine is responsible for the symptoms of an allergic reaction. It causes pain and itching, dilates capillaries and makes them more permeable, leading to red skin and swelling. Heparin is an anticoagulant, it prevents blood from clotting. Magnification: x4,800 when printed at 10 centimetres wide.
New to Writers Site?
Have You Reached this Page from Outside the NutriScape Network?
If so, you might be puzzled. The purpose of the Writers site is to provide dietitians in every niche with an opportunity to promote their independent businesses through Writing Articles within their specialty.
You Have Reached an Article Request Page: By publishing articles on NutriScape.NET, Dietitians can link to their own website or social media pages through the biography. We believe in Crowdsourcing. When RD/RDNs band together through The NutriScape Project, we can build a better future for all of us!
How to Use These Article Ideas

 Scan Me!
Scan Me!